This post is directed to WebLearn site maintainers
– Have students reported that they cannot see certain materials in WebLearn?
– Do some links in your WebLearn sites appear to be broken?
– Are videos or other content missing from your WebLearn pages?
If the answer to these questions is ‘yes’, this may be the result of changes to the way web browsers handle non-secure content. This blog post explains, in non-technical terms, what has changed and what you need to do to fix the ‘broken’ links permanently, or reinstate missing content.
Background
Web browsers classify content as either secure or non-secure.
- With secure content, the URL begins with the protocol https://
- With non-secure content, the URL begins with the protocol http://
A web page can contain solely secure content, solely non-secure content, or a mixture (‘mixed content’).
The major web browsers have recently changed the way in which they handle non-secure content. They now prevent you from displaying non-secure content within a secure page ( such as WebLearn) (e.g. via an embedded webpage, video, iframe, or a widget such as an old Twitter feed or Facebook). This can affect how links are displayed (or not) in WebLearn sites, so you need to take remedial action. The benefit is that your WebLearn sites will be more secure and less susceptible to malicious attacks that can potentially occur via a piece of non-secure content.
What you need to do
The WebLearn team has made it possible temporarily to display certain non-secure content in some tools (see ‘Additional information’ below), while a user is viewing the page. However, for a permanent solution site maintainers need to edit any non-secure links in their sites.
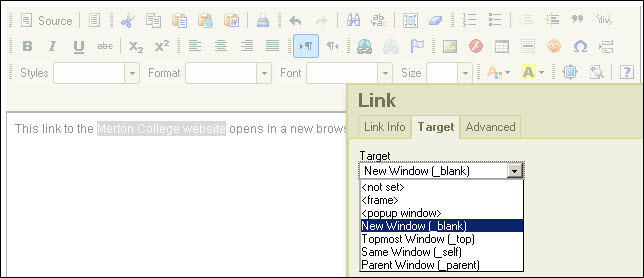
- Make all hyperlinks that currently point to non-secure (http://) sites open in a new browser tab or window. Use the WYSIWYG editor to edit each link and change the Target to ‘New Window (_ blank)’:
- If the site’s Home page points to a Site Info URL (i.e. the Home page has not been created using the built-in WYSIWYG editor), the target page must be a secure one (i.e. https://).If the URL begins with http:// and no https:// version exists (e.g. it’s the home page of a college or department), the link will no longer work. You will need to rethink the site’s Home page and perhaps create one using the built-in WYSIWYG editor.
- If the site contains links to YouTube or Vimeo videos (or similar), update the links to use the new embed code that is provided by the host sites, as follows:
- Go to the webpage of the original video, click ‘Share’ and then ‘Embed’ to copy the new code (note: it should provide the specifications for the video, something like this: ‘<iframe width=”560″ height=”315″ src=”//www.youtube.com/embed/bqM1bAO5Bzo” frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen></iframe>’).
- If the host site does not provide an https:// version of the ’embed’ code (e.g. www.dailymotion.com), then create a WebLearn page containing a link to the required video, to open in a new window.
- If the site contains embedded widgets, do one of the following:
- Switch to the https:// version, if one exists;
- Open the link in a new window; or
- Remove the widget altogether.
What you need to be aware of
If you (or other users of your site) encounter any of the following situations, it means that WebLearn is still finding mixed content. Check the links and, if necessary, edit them as described above.
- A page that you had expected to open within the current WebLearn page opens in a new tab or window instead, or alternatively it doesn’t open at all.
This is probably because the link is to non-secure content (http://). If you want a page to open within the current WebLearn page, then it must point to an https:// target. - Content is blocked: i.e. a page is not displayed, or a page is displayed, but some of its elements are missing (e.g. videos or widgets).
When viewing the webpage, look out for either a small grey shield in the browser bar (Firefox or Chrome) or a yellow ‘warning’ box at the bottom (Internet Explorer 9 or 10). Click the icon or box and decide whether to view some or all of the blocked content.
Note: You may still see the grey shield (yellow box) even if some of the content is visible. This is because WebLearn has ‘rewritten’ the web page after the browser displayed the shield (or box).
Additional information
The WebLearn tools in which non-secure content is temporarily displayed are: Resources, Web Content, Home, Forums and the Wiki.
Examples of non-secure content which is temporarily displayed are: YouTube and Vimeo videos.
The following blog posts provide full technical details of the changes described above:
(where these posts mention ‘rewritten on-the-fly’ or ‘dynamically rewritten’ it means that the content is temporarily displayed. Note that site owners still need to edit mixed content for a permanent solution.)